Throughout history, people have chewed everything: from resin and paraffin wax to Orbit. For example, 5,000 years ago people used to chew pieces of birch bark tar.
Tar has antiseptic properties and other medicinal effects, just like modern chewing gum. Obviously, there is more to this habit than a fresh breath or unusual distraction. Much more, it seems.
We untangled some myths from reality about the effect chewing gum can have on your body and is happy to share the results.
Chewing Gum Effects On The Body
6. It Affects Your Teeth
 © depositphotos.com
© depositphotos.com
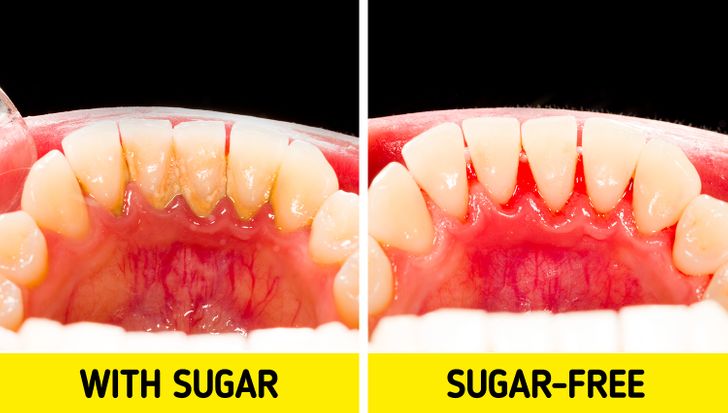
Good: Sugar-free gum is an effective bacteria killer, which can give toothpaste a run for its money.
Protects your teeth against cavities and gingivitis, activating the extra saliva that removes acids and food debris.
It also strengthens the enamel by applying additional calcium and phosphate.
Bad: but if your gum contains sugar, it has a negative impact on oral health. Bacteria that live in the oral cavity digest sugar before it reaches the stomach, causing plaque buildup on your teeth. It also increases tooth decay over time.
5. It Improves Memory
Nibbling on gum increases heart rate, blood flow, and oxygen supply to the brain. One of the positive effects of this is the cognitive boost we experience: it improves alertness, thought processing, decision making, and memory.
Unfortunately, it doesn’t work long-term, it only works if you chew before or during particularly challenging tasks.
4. It Aids In Weight Loss
 © depositphotos.com, © depositphotos.com
© depositphotos.com, © depositphotos.com
Good: chewing gum can sometimes suppress our appetite. After chewing gum in the morning, people tend to feel less hungry.
It’s sweet and low in calories, so it can help you cut down on snacking. It also increases energy expenditure, speeds up your metabolism, and makes you feel less tired after eating.
Bad: But chewing gum’s reputation as a dietary aid can backfire in a bad way. The chewing motion and constant saliva trick your brain to think that you are very hungry.
And peppermint gum leads you to go for junk food, rather than healthier options like fruit because the taste is horrible. Bubblegum chewers also tend to eat fewer meals a day but load up on calories when they do eat.
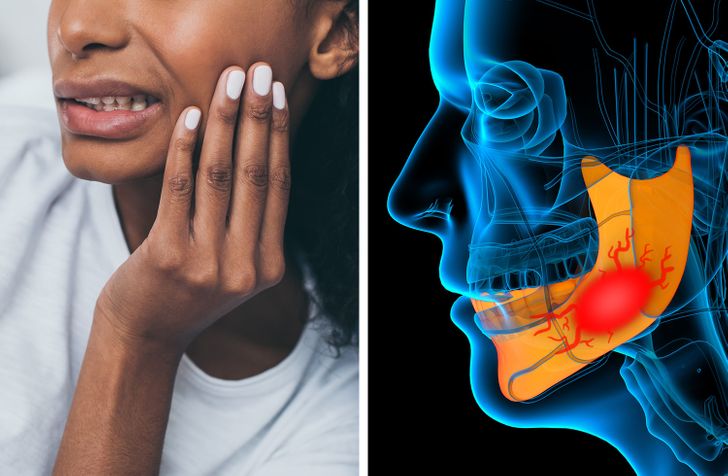
3. It Causes Jaw Problems
 © depositphotos.com, © depositphotos.com
© depositphotos.com, © depositphotos.com
Constant chewing can lead to a disorder that affects the jaw joints and surrounding muscles. Any movement of the jaw (eating, laughing, or even talking) is accompanied by severe pain that sometimes spreads to the neck and shoulders.
The risk is especially high if you chew during times of stress, as people tend to unconsciously clench their teeth when nervous.
2. It Influences The Digestive System
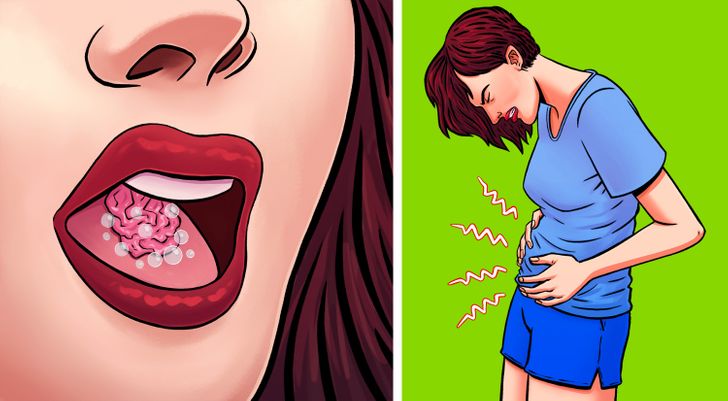
Good: the extra saliva production when chewing gum effectively helps against morning motion sickness.
Some say it works better than medications, reducing the chances of vomiting, abdominal discomfort, and nausea just as quickly, as well as being considerably cheaper and more available.
Bad: But woe to you if you have a sensitive stomach or indigestion! When you chew, always swallow small sips of air and fill your stomach with gas that can cause bloating.
The sugar alcohols that are often used as sweeteners act as purgatives, causing cramps, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
1. It Impacts Your Brain
 © depositphotos.com, © depositphotos.com
© depositphotos.com, © depositphotos.com
Good: surprisingly, chewing gum has super anti-stress powers and improves mood.
Munching this stuff reduces levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, and simply chewing is relaxing for most people. Dispel anxiety and fatigue and elevate our mood during the day.
Bad: But constant pressure on the jaw increases the number and frequency of migraines and tension headaches.
In the worst case, it can lead to chronic headaches. So if you’re already predisposed to migraines, it’s best to avoid gum altogether.
Do you like to chew gum? Have you noticed any changes in your body with this?









